What is Photodynamic Therapy?
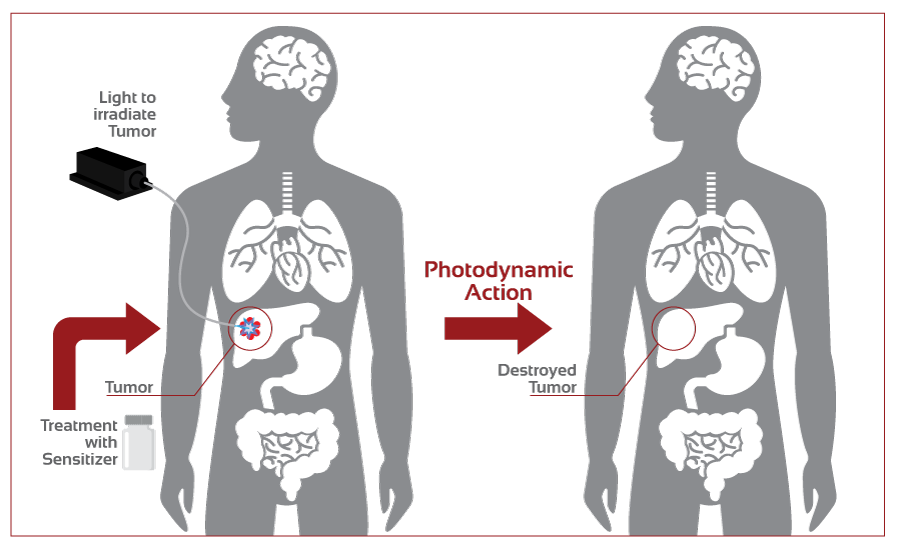
Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) is a treatment that uses special drugs called photosensitizing agents, along with light, to kill cancer cells and treat certain skin condition. These photosensitizing agents only work after they have been activated or “turned on” by specific wavelengths of light.
Depending on which part of the body is being treated, the photosensitizing agent is either injected into the bloodstream or applied directly onto the skin. Over a certain amount of time the drug is absorbed by the cancer cells. Light is then applied to the treatment area using an optical fiber.
The light triggers a photochemical reaction but does not cause any heat damage. Instead, it causes the drug to react with oxygen, which forms a chemical that kills the targeted cells. PDT also helps by destroying blood vessels that feed cancer cells and by alerting the immune system to attack the cancer.
Arktis Laser offers a wide range of fiber coupled laser light sources that are ideally suited for PDT.
The most common wavelengths used in PDT are between 633nm-760nm (depending on the photosensitizing agent used) with typical fiber coupled output powers between 500mW and 2W.
Pros and Cons of PDT
Studies have shown that PDT can work as well as surgery or radiation therapy in treating certain kinds of cancers and pre-cancers. It has several advantages over traditional treatments:
But PDT has limits too:
Photosensitizer Properties
The ideal PDT photosensitizer has the following characteristics:
Properties of some photosensitizer dyes approved for PDT treatment and used in PDT-related clinical trials:
Compound |
Trademark |
λmax (nm) |
ΦΔ |
Application |
Arktis Laser Wavelengths Available |
Porfimer sodium |
Photofrin |
632 (3000) |
0.89 |
Canada (1993)—bladder cancer; USA (1995)—esophogeal cancer; USA (1998)—lung cancer; USA (2003)—Barrett’s esophagus; Japan—cervical cancer; Europe, Canada, Japan, USA, UK—endobroncheal cancer |
|
5-Aminolevulinic acid (ALA) |
Levulan |
632 (5000) |
0.56 |
USA (1999)—actinic keratosis |
- |
Methyl aminolevulinate (MAL) |
Metvixia |
– |
– |
USA (2004)—actinic keratosis |
- |
Hexaminolevulinate (HAL) |
Cysview |
– |
– |
USA (2010)—bladder cancer diagnosis |
- |
Benzoporphyrin derivative monoacid ring A (BPD-MA) |
Visudine |
689 (34,000) |
0.84 |
USA (1999)—age-related macular degeneration |
|
Meta-tetra(hydroxyphenyl)chlorin (m-THPC) |
Foscan |
652 (35,000) |
0.87 |
Europe-neck and head cancer |
|
Tin ethyl etiopurpurin |
Purlytin |
664 (30,000) |
– |
Clinical trials—breast adenocarcinoma, basal cell carcinoma, Kaposi's sarcoma, age-related macular degeneration |
|
N-aspartyl chlorin e6 (NPe6) |
Laserphyrin, Litx |
664 (40,000) |
0.77 |
Japan (2003)-lung cancer |
- |
2-(1-Hexyloxyethyl)-2-devinyl pyropheophorbide (HPPH) |
Photochlor |
665 (47,000) |
– |
Clinical trials—esophogeal cancer, basal cell carcinoma, lung cancer, Barrett’s esophagus |
- |
Palladium bacteriopheophorbide (WST09) |
Tookad |
763 (88,000) |
0.50 |
Phase IV clinical trials for prostate cancer as of Feb 2019 *Showing promising results. Predicted to grow in popularity |
|
WST11 |
Stakel |
– |
– |
Clinical trials—prostate cancer |
- |
Motexafin lutetium (Lu-Tex) |
Lutrin, Optrin, Antrin |
732 (42,000) |
– |
Clinical trials—prostate cancer, age-related macular degeneration, breast cancer, cervical cancer, arterial disease |
|
Aluminum phthalocyanine tetrasulfonate (AlPcS4) |
Photosens |
676 (200,000) |
0.38 |
Russia (2001)—stomach, skin, lips, oral cavity, tongue, breast cancer |
|
Silicon phthalocyanine (Pc4) |
– |
675 (200,000) |
– |
Clinical trials—actinic keratosis, Bowen’s disease, skin cancer, mycosis fungoides |
Examples of non-porphyrin PDT candidates. None have received FDA approval for their application areas:
Compound |
λmax(nm) |
εmax (M−1cm−1) |
Application |
Arktis Laser Wavelengths Available |
Hypericin |
590 |
44,000 |
squamous cell carcinoma, basal cell carcinoma |
|
Methylene blue |
666 |
82,000 |
melanoma, basal cell carcinoma, Kaposi’s sarcoma, chronic periodontitis |
|
Toluidine blue |
630 |
51,000 |
chronic periodontitis |
|
Rose bengal |
549 |
100,000 |
breast carcinoma, melanoma |
|
TH9402 |
514 |
100,000 |
graft-versus-host disease |
|
Merocyanine 540 |
556 |
110,000 |
leukemia, lymphoma |
|
Curcumin |
420 |
55,000 |
oral disinfectant |
| Product | Wavelength | Description | Starting At | In Stock | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 | 633 nm | 633 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 5 - 80 mW Output Power | $3,060.00 | Specs |
|
 | 635 nm Best Seller! | 635 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 5 - 500 mW Output Power | $2,225.00 | Specs |
|
 | 635 nm Best Seller! | 635 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 3000 - 6000 mW Output Power | $5,913.00 | Specs |
|
 | 655 nm | 655 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 5 - 1000 mW Output Power | $1,798.00 | Specs |
|
 | 655 nm | 655 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 5000 - 5000 mW Output Power | $11,338.00 | Specs |
|
 | 690 nm | 690 nm Collimated Diode Laser System 100 - 800 mW Output Power | $3,615.00 | Specs |
|
 | 760 nm | 760 nm Low-Noise Collimated Diode Laser System 5 - 5000 mW Output Power | $4,942.00 | Specs |